Building a shed is a fantastic way to add storage or workspace to your backyard. However, a shed is only as strong as the foundation it sits on. If you're looking for inexpensive and practical shed foundation ideas for your backyard, you've come to the right place. In this guide, I’ll share various cost-effective shed foundation options, their benefits, and how to build them, based on my experiences and insights from research.

Understanding Shed Foundation Types
There are two primary categories for shed foundations: on-grade and frost-proof. Choosing the right type depends on your shed size, local climate, soil type, and budget.
On-Grade Foundations
An on-grade or "floating" foundation sits directly on the ground without requiring deep digging or concrete pouring. This type is ideal for small to medium-sized sheds and is quick and easy to construct. They are also moveable, making them a versatile choice for those who might relocate their shed.
Frost-Proof Foundations
Frost-proof or "permanent" foundations are more durable and are essential in regions with frost heave. This type of foundation requires digging below the frost line and using concrete or other stable materials. Frost-proof foundations are best suited for larger sheds or areas with harsh weather conditions.
Inexpensive Shed Foundation Ideas
Now, let’s delve into the most cost-effective shed foundation options for your backyard. These foundations provide solid support without breaking the bank.
1. Concrete Block Foundation

Concrete blocks are a popular and affordable on-grade foundation option. They are easy to install, require minimal materials, and provide good support for small to medium-sized sheds.
Pros:
- Low cost and easy to find.
- Simple installation process.
- Allows for easy leveling on slightly uneven ground.
Cons:
- Not suitable for larger sheds or areas with frost heave.
- Over time, blocks may shift or settle.
How to Build:
- Clear and level the area where your shed will be placed.
- Lay a base of gravel and compact it with a hand tamper.
- Place concrete blocks in rows, spaced evenly to support the shed’s frame.
- Ensure each block is level, adding or removing gravel as needed.
2. Skid Foundation
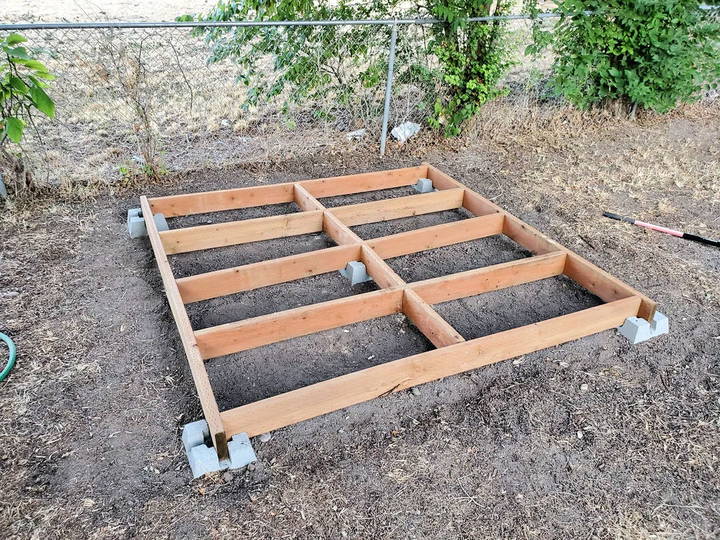

A skid foundation involves placing large, pressure-treated wooden beams (or "skids") directly on the ground. This type has been used for centuries and remains a favorite for its simplicity and effectiveness.
Pros:
- Quick and easy to construct.
- Ideal for small sheds.
- The shed can be moved if needed.
Cons:
- Not suitable for uneven or sloped terrain.
- Wood in contact with the ground can rot over time.
How to Build:
- Lay down a layer of gravel and compact it.
- Position two or more pressure-treated beams parallel to each other.
- Build the shed floor frame directly on top of the skids.
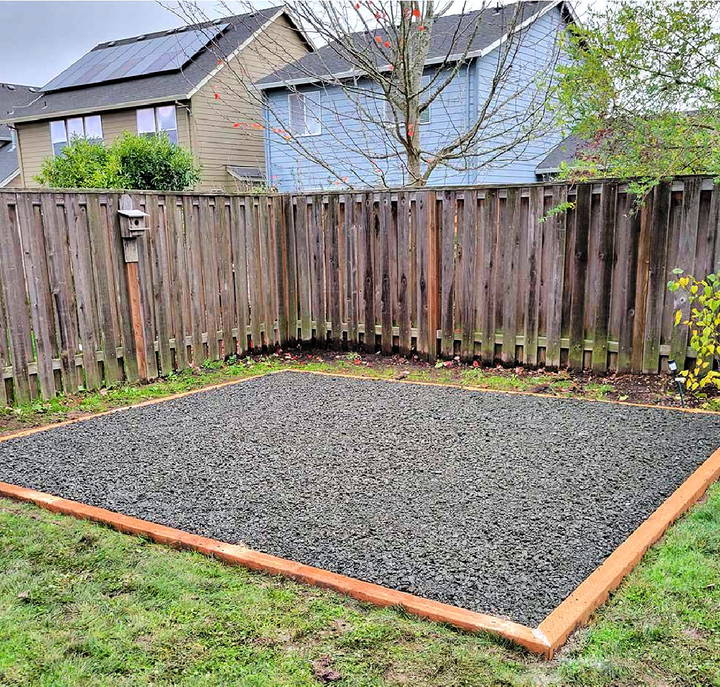
3. Gravel (Crushed Stone) Pad

A gravel pad is one of the best all-around options for shed foundations. Gravel is cost-effective, provides excellent drainage, and is easy to work with. When combined with a lumber perimeter, it becomes even more stable.
Pros:
- Good drainage prevents water damage.
- Supports all parts of the shed structure equally.
- Works well on slightly sloped sites with proper preparation.
Cons:
- More labor-intensive than some other options.
- May require additional materials like treated lumber or concrete piers for reinforcement.
How to Build:
- Excavate the area to a depth of about 4-6 inches.
- Install a perimeter of treated lumber, securing the corners with screws or brackets.
- Fill the area with 3/4-inch crushed stone or gravel, and compact it using a tamper or plate compactor.
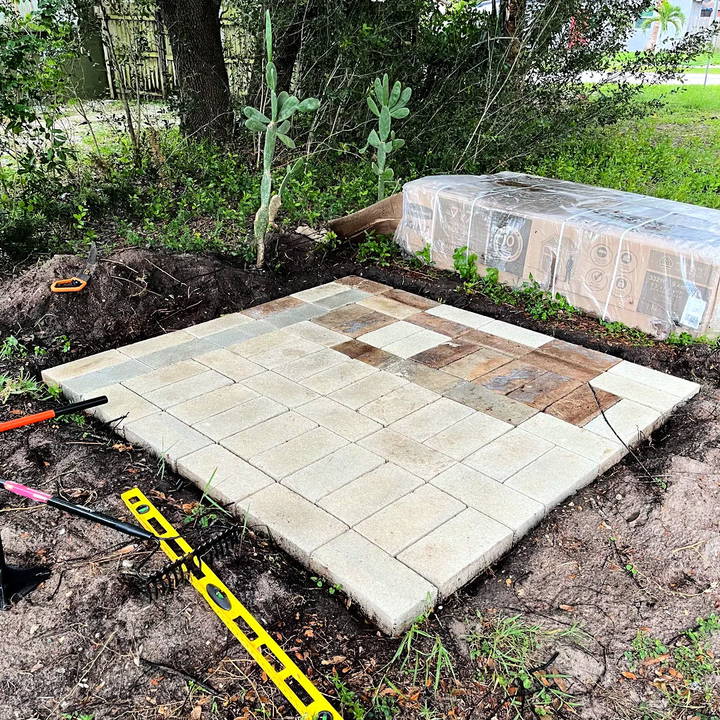
4. Paver Foundation
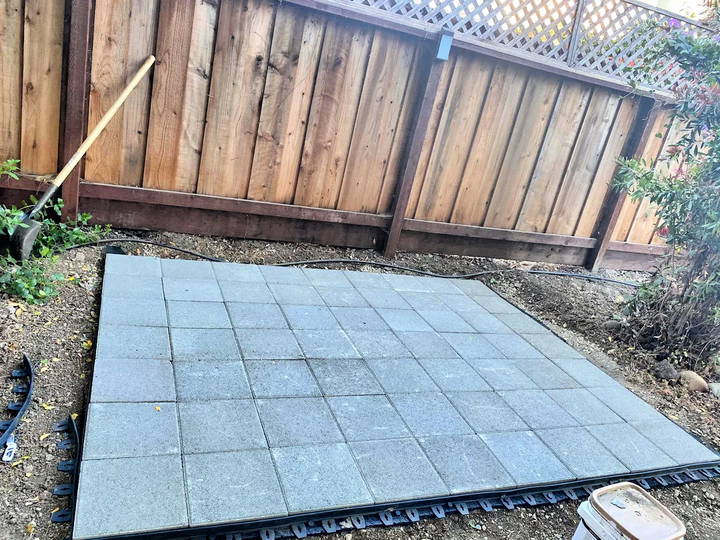

Paver foundations are similar to concrete blocks but use smaller paving stones or bricks. They are an excellent choice for sheds with built-in floors or smaller sheds that need a stable base.
Pros:
- Aesthetically pleasing.
- Easy to level and install.
- Suitable for small sheds.
Cons:
- Not recommended for sloped sites.
- Pavers can shift or sink over time.
How to Build:
- Level the ground and lay a base of compacted gravel.
- Arrange the pavers in the desired pattern, ensuring they are level.
- Fill gaps with sand and compact again to secure.
5. Plastic Grid Foundation

Plastic grid systems are a newer and environmentally friendly option for shed foundations. They consist of interlocking plastic grids filled with gravel, providing a stable, permeable surface.
Pros:
- Lightweight and easy to handle.
- Provides excellent drainage.
- Simple to install.
Cons:
- Limited availability.
- May not support larger sheds without additional reinforcement.
How to Build:
- Level the ground and lay down a layer of landscaping fabric.
- Snap the plastic grids together and place them on the prepared site.
- Fill the grids with gravel and compact.
6. Deck Block Foundation
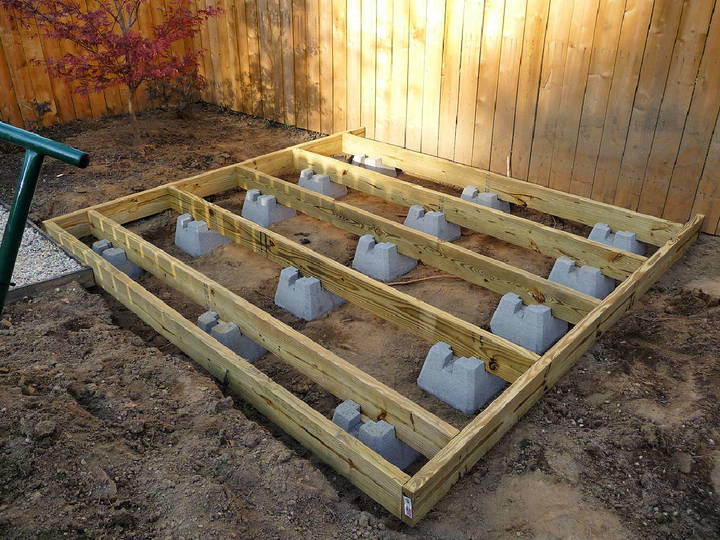

Deck blocks, also known as pier blocks, are concrete blocks designed to support beams and joists for a shed floor. They are another inexpensive option that offers flexibility in placement.
Pros:
- Provides elevation, reducing exposure to moisture.
- Easy to install and level.
- Can be used on slightly uneven ground.
Cons:
- Not suitable for large sheds or heavy loads.
- May not meet local building codes for permanent structures.
How to Build:
- Level the area and lay down gravel for drainage.
- Position deck blocks in a grid pattern to support the shed floor joists.
- Install the shed floor frame on top of the deck blocks.
Choosing the Right Foundation for Your Shed
Selecting the best foundation for your shed depends on various factors, including the shed size, the slope of your yard, soil conditions, and your budget. Here’s a quick guide to help you decide:
For Small Sheds (Under 8’x8’):
- Concrete blocks or pavers work well.
- Skid foundations are also a great, moveable option.
Medium Sheds (8’x12’ to 10’x16’):
- Gravel pad or deck blocks provide more support.
- Consider plastic grid systems if drainage is a concern.
Large Sheds (Over 10’x16’):
- Gravel pad combined with concrete piers or footers is ideal.
- Consider a full concrete slab for the most durable foundation.
Sloped or Uneven Sites:
- Gravel pads can be modified to accommodate slopes.
- Screw piles or post-and-beam foundations offer flexibility in height.
For Frost-Prone Areas:
- Frost-proof options like concrete piers or a monolithic concrete slab are essential to prevent shifting.
Final Thoughts
Building a strong foundation is crucial for the longevity of your shed. While there are many foundation options available, choosing an inexpensive yet effective method can save you money and effort in the long run. Whether you opt for a simple gravel pad or a concrete block setup, make sure your foundation is solid, level, and appropriate for your climate and soil conditions.
Investing the time and resources in the right foundation will ensure your shed stands sturdy and remains a valuable addition to your backyard for years to come.
FAQ: Shed Foundation Essentials
Discover essential shed foundation tips for stability and longevity. Learn how to choose the right materials and prepare your site effectively.
What is the difference between on-grade and frost-proof foundations?
On-grade foundations sit directly on the ground and are easier to build, ideal for small sheds. Frost-proof foundations require digging below the frost line, offering durability in cold climates, and are necessary for larger, more permanent sheds.
Can I build a shed foundation on a slope?
Yes, gravel pads, screw piles, and post-and-beam foundations work well on slopes. Ensure proper leveling and drainage to prevent shifting or water pooling around the shed.
How do I prevent wood skids from rotting?
Use pressure-treated lumber rated for ground contact. Elevate skids on a gravel base to improve drainage, reducing the risk of wood rot and extending the lifespan of your foundation.
Do I need to anchor my shed to its foundation?
Yes, anchoring prevents movement during high winds or severe weather. Concrete piers, metal anchors, and ground screws are effective options for securing your shed to its foundation.
How thick should a gravel pad be for a shed foundation?
A gravel pad should generally be 4 to 6 inches thick, compacted in layers. This thickness provides stability, good drainage, and adequate support for most shed sizes.
What foundation type is best for heavy equipment storage?
A poured concrete slab or concrete foundation with footers is ideal for heavy equipment. It provides a level, durable surface that can bear substantial weight and withstand long-term use.
Can I use pavers for a large shed foundation?
Pavers are best for small sheds. For larger sheds, they may shift or sink over time. Consider gravel pads, concrete piers, or other more stable options for better support and durability.